Introduction
How To Know If You Have Bed Bugs? Detecting bed bugs early is crucial for preventing a small problem from becoming a significant infestation. Bed bugs are notorious for their rapid reproduction and elusive nature, making early identification essential. This guide aims to provide you with the knowledge and tools needed to identify bed bug infestations in your home.
Bed bugs are tiny, nocturnal insects that feed on human blood. They are challenging to spot due to their small size and tendency to hide in dark, secluded places. Understanding the signs of a bed bug infestation can save you time, money, and stress. Knowing what to look for will help you act quickly and effectively.
The presence of bed bugs can cause anxiety and discomfort, not just physical but also psychological. Recognizing the signs early allows for prompt action, reducing the impact on your daily life. From identifying physical evidence like bites and stains to understanding their common hiding spots, this guide covers it all.
Early detection is vital because bed bugs can spread quickly within your home. They can hide in furniture, clothing, and even electrical outlets. By learning how to identify bed bugs, you can prevent a minor issue from escalating into a severe infestation. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), understanding the life cycle and habits of bed bugs is key to effective control.
In the following sections, we will delve into the specifics of bed bug identification. We will explore their biology, the common signs of an infestation, and the best methods for inspection. Additionally, we will provide tips on confirming their presence and outline the next steps if you discover bed bugs in your home. ….Click Now to Read More Bed Bug Articles!
Understanding Bed Bugs
To effectively deal with bed bugs, it’s essential to understand what they are, their life cycle, and common misconceptions. This foundational knowledge helps in identifying and eradicating these pests.
What Are Bed Bugs?
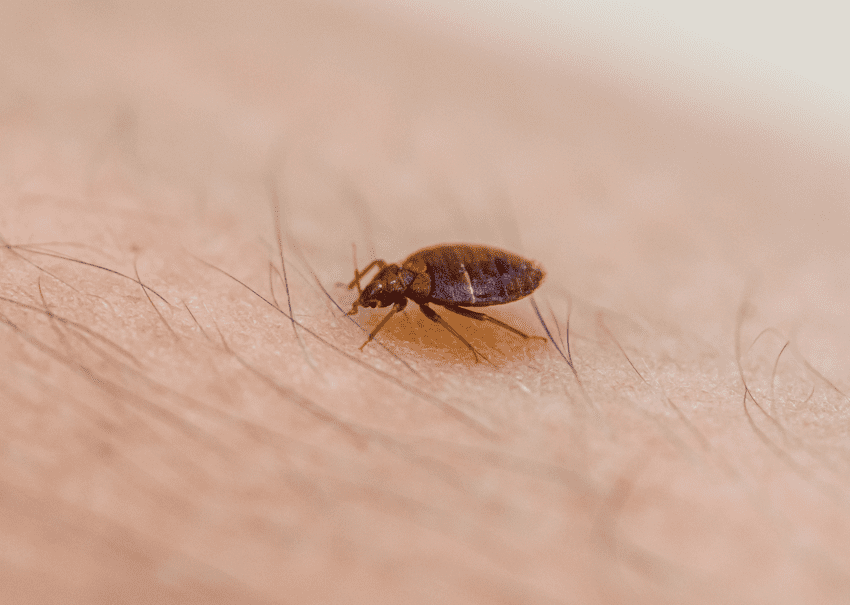

Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, reddish-brown insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are wingless and can range from 1 to 7 millimeters in length. Bed bugs are primarily active at night and hide in cracks and crevices during the day. Despite their small size, they are visible to the naked eye.
Bed Bug Life Cycle
Understanding the bed bug life cycle is crucial for effective detection and control. Bed bugs undergo three main stages: egg, nymph, and adult.
- Eggs: Female bed bugs lay eggs in secluded areas. Each egg is about the size of a pinhead and takes about 6 to 10 days to hatch.
- Nymphs: After hatching, bed bug nymphs go through five growth stages, molting after each one. Nymphs require a blood meal to molt and grow. This stage lasts about five weeks.
- Adults: Adult bed bugs are oval, flattened, and reddish-brown. They can live for several months, with females laying hundreds of eggs in their lifetime.
Recognizing these stages helps in identifying bed bug presence at different points in their life cycle.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Several myths and misconceptions surround bed bugs, leading to ineffective control methods. It’s essential to debunk these myths for accurate identification and treatment.
- Myth 1: Bed Bugs Only Infest Dirty Homes: Bed bugs can infest any home, regardless of cleanliness. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide, not filth.
- Myth 2: Bed Bugs Transmit Diseases: Bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases to humans. However, their bites can cause itching, allergic reactions, and secondary infections.
- Myth 3: Bed Bugs Are Too Small to See: Although bed bugs are small, they are visible to the naked eye, especially in their adult stage. Their eggs and nymphs, while smaller, can also be seen upon close inspection.
For more detailed information on bed bugs and their behavior, refer to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) resource. Understanding these aspects of bed bugs is the first step in effective detection and control. By dispelling myths and learning about their life cycle, you can better identify and manage a bed bug infestation.
Signs of a Bed Bug Infestation
Identifying the signs of a bed bug infestation early can prevent significant issues later. Bed bugs leave several telltale signs that can help you determine their presence in your home.
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence is often the first indication of a bed bug problem. Knowing what to look for can help you act quickly.
- Bed Bug Bites: Bed bug bites are usually red, itchy welts that appear in a line or cluster. These bites often occur on exposed skin areas such as the face, neck, arms, and hands. However, not everyone reacts to bed bug bites, so the absence of bites does not necessarily mean you are bed bug-free.
- Blood Stains on Sheets: After feeding, bed bugs may leave small blood stains on your sheets, pillowcases, and mattresses. These stains are usually dark red or rust-colored and can be easily spotted.
- Bed Bug Excrement: Bed bug feces appear as small, dark spots about the size of a pinhead. You can find these spots on mattresses, bed linens, and nearby furniture. The spots can smear like a marker when wiped.
Visual Sightings
Spotting live bed bugs or their remnants is a clear sign of an infestation.
- Live Bed Bugs: Adult bed bugs are flat, oval, and reddish-brown. They are often found in mattress seams, box springs, bed frames, and headboards. During the day, they hide in cracks and crevices, making them difficult to spot without a thorough inspection.
- Bed Bug Shells and Molted Skins: As bed bugs grow, they shed their exoskeletons. These shells are pale yellow and can be found in areas where bed bugs hide. Finding these remnants indicates an active bed bug population.
- Bed Bug Eggs and Nymphs: Bed bug eggs are tiny, white, and about the size of a pinhead. Nymphs, or immature bed bugs, are smaller and lighter in color than adults. You can find eggs and nymphs in the same hiding places as adult bed bugs.
Unusual Odors
Bed bugs emit a distinctive odor, which can be a sign of a large infestation.
- Sweet, Musty Smell: A strong, sweet, musty odor can indicate a significant bed bug infestation. This smell comes from bed bug pheromones and is often compared to the scent of overripe raspberries.
- Where to Detect These Odors: You might notice this odor near bed bug hiding places, such as mattresses, bed frames, and upholstered furniture. If you detect an unusual smell, it’s essential to conduct a thorough inspection.
Recognizing these signs can help you identify a bed bug infestation early. For more information on identifying bed bug signs, visit the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guide. Early detection and prompt action are key to controlling and eliminating bed bugs from your home.
Common Bed Bug Hiding Places
Bed bugs are experts at hiding in small, dark places, making them difficult to detect. Knowing where they hide can help you find and eliminate them more effectively. Bed bugs can hide in various areas of your home, often close to where you sleep or rest.
Furniture and Bedding
Bed bugs prefer to stay close to their food source, which is often your bed.
- Mattresses and Box Springs: Bed bugs commonly hide in the seams, tufts, and folds of mattresses and box springs. Check around the piping, tags, and under any loose fabric.
- Bed Frames and Headboards: Bed bugs can hide in the crevices and joints of bed frames and headboards. Wooden frames are particularly vulnerable due to the number of potential hiding spots.
Household Items
Apart from beds, bed bugs can infest other household items.
- Upholstered Furniture: Sofas, recliners, and other upholstered furniture can harbor bed bugs. Look in the seams, tufts, skirts, and between cushions.
- Curtains and Drapes: Bed bugs can climb up fabric surfaces. Check the folds, hems, and edges of curtains and drapes.
- Carpets and Rugs: Bed bugs can hide in the fibers of carpets and rugs, especially near the edges and under furniture.
Other Hidden Spots
Bed bugs are adept at finding hiding places that are not immediately obvious.
- Wall Cracks and Baseboards: Small cracks in walls and gaps in baseboards provide excellent hiding spots for bed bugs. Inspect any visible crevices and gaps around your home.
- Electrical Outlets and Appliances: Bed bugs can hide behind electrical outlet covers and inside appliances. Remove outlet covers carefully and check for signs of bed bugs.
For more details on identifying common bed bug hiding places, refer to the National Pest Management Association (NPMA) resource. Understanding where bed bugs are likely to hide is crucial for a thorough inspection and effective treatment. Identifying and targeting these hiding spots can help you eradicate bed bugs from your home more efficiently.
Inspection Techniques
Effective inspection techniques are crucial for identifying bed bug infestations accurately. Both do-it-yourself (DIY) and professional inspections have their benefits, and knowing how to conduct each can help you address the issue promptly.
DIY Inspection
Performing a DIY inspection can save time and money, and it’s a good first step if you suspect a bed bug problem.
- Tools Needed: Gather a flashlight, magnifying glass, gloves, and a credit card or similar flat tool. These items will help you see into small spaces and crevices where bed bugs might hide.
- Step-by-Step Inspection Process:
1. Inspect Your Bed: Start with the mattress and box springs. Use the flashlight and magnifying glass to check seams, folds, and tags. Use the credit card to check cracks and crevices.
2. Examine Furniture: Look at upholstered furniture, paying attention to seams, tufts, and skirts. Check between cushions and under the furniture.
3. Check Other Areas: Inspect curtains, carpets, and rugs, especially along the edges and under furniture. Look at wall cracks, baseboards, and behind electrical outlet covers.
4. Look for Signs: As you inspect, keep an eye out for live bed bugs, shells, molted skins, eggs, fecal spots, and blood stains.
Professional Inspection
Sometimes, a professional inspection is necessary, especially for severe infestations or if you’re unable to locate the bed bugs yourself.
- When to Call an Exterminator: Call a professional if you find evidence of bed bugs but can’t locate the infestation, if the infestation is extensive, or if you prefer expert assistance.
- What to Expect from a Professional Inspection: Professionals use advanced tools and techniques to detect bed bugs. They may use canine inspection, where trained dogs sniff out bed bugs with high accuracy. Professionals will also provide a detailed inspection report and a recommended treatment plan.
For more information on professional bed bug inspections, visit the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) resource. Combining DIY and professional inspections can give you a comprehensive understanding of your bed bug situation, helping you decide the best course of action. Conducting thorough inspections ensures you identify all hiding places and take the necessary steps to eliminate the infestation.
Confirming Bed Bug Presence
Confirming the presence of bed bugs is a critical step before proceeding with treatment. Proper identification helps distinguish bed bugs from other pests and ensures that the right measures are taken.
Differentiating from Other Pests
Bed bugs can be confused with other pests such as fleas and mites. Knowing the differences can prevent misidentification.
- Fleas vs. Bed Bugs: Fleas are smaller than bed bugs and have a more elongated body. They are typically found on pets and their bedding. Unlike bed bugs, fleas can jump long distances. Bed bug bites appear in clusters or lines, while flea bites are often scattered.
- Mites vs. Bed Bugs: Mites are microscopic and usually associated with dust or animals. They do not leave visible signs like bed bugs do. Bed bug infestations are characterized by visible bugs, molted skins, and fecal spots, which are not seen with mites.
Laboratory Confirmation
In some cases, professional lab confirmation may be needed to ensure accurate identification.
- Sample Collection: Collect samples of the suspected bed bugs, their eggs, or their molted skins. Place them in a sealed plastic bag or small container. Ensure that the samples are intact and not crushed.
- Sending Samples to Labs: Send the collected samples to a professional pest identification lab. Many universities and pest control companies offer this service. Lab analysis can confirm whether the samples are indeed bed bugs. This confirmation can guide the appropriate treatment measures.
For more information on confirming bed bug presence, refer to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guide. Proper identification and confirmation of bed bugs are essential steps in managing an infestation. By differentiating bed bugs from other pests and utilizing professional lab services when necessary, you can ensure that the right steps are taken to address the issue effectively.
Next Steps After Identification
Once you have confirmed the presence of bed bugs, taking immediate and appropriate action is crucial to control and eliminate the infestation. The following steps outline how to manage a bed bug problem effectively.
Immediate Actions
Taking prompt measures can help contain the infestation and prevent it from spreading further.
- Isolating Affected Areas: Start by isolating the infested areas. Enclose mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof covers. Avoid moving infested furniture to other rooms, as this can spread the bugs. If possible, quarantine the affected room until treatment is complete.
- Preventing Spread: Reduce the risk of spreading bed bugs by minimizing clutter. Seal infested items in plastic bags until they can be cleaned or treated. Wash and dry bedding, curtains, and clothing on high heat. Vacuum regularly and dispose of the vacuum bag immediately after use.
Treatment Options
Different treatment options are available for bed bug infestations, ranging from DIY methods to professional extermination services.
- DIY Treatment Methods: For minor infestations, DIY treatments can be effective. Use bed bug sprays and diatomaceous earth to treat cracks, crevices, and other hiding spots. Place bed bug interceptors under the legs of beds and furniture to trap and monitor bed bugs. Regularly wash and heat-treat infested items.
- Professional Extermination Services: For severe infestations, professional pest control services are recommended. Exterminators use methods such as heat treatments, chemical treatments, and fumigation to eliminate bed bugs. They also provide follow-up inspections to ensure the infestation is fully eradicated.
Prevention Tips
Preventing future infestations is key to maintaining a bed bug-free home.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of your home, especially after traveling or bringing in second-hand furniture. Early detection can prevent a full-blown infestation.
- Protective Measures for Your Home: Use bed bug-proof mattress and pillow encasements. Keep your home clean and free of clutter. Seal cracks and crevices in walls and furniture where bed bugs can hide. Be cautious when purchasing used furniture, and thoroughly inspect items before bringing them into your home.
For more detailed information on bed bug treatment and prevention, visit the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) resource. Taking these steps after identifying bed bugs can help you control and eliminate the infestation effectively. Immediate actions, combined with appropriate treatment and preventive measures, ensure that your home remains free from bed bugs.
Conclusion
Detecting and managing bed bug infestations requires knowledge, vigilance, and timely action. This guide has equipped you with the essential tools and information needed to identify and address bed bug problems effectively.
Recap of Key Points
Early detection is critical in preventing bed bugs from spreading and causing more significant issues. By understanding what bed bugs are, recognizing the signs of an infestation, and knowing where they typically hide, you can take the necessary steps to confirm their presence. Employing effective inspection techniques, both DIY and professional, ensures accurate identification.
Encouragement to Act Quickly
If you suspect a bed bug infestation, act immediately. Isolate the affected areas and take measures to prevent the spread. Choose the appropriate treatment option, whether DIY methods for minor issues or professional extermination for more severe infestations. Regular inspections and preventive measures are crucial in keeping your home bed bug-free.
Resources for Further Assistance
For additional information and support, consider the following resources:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – Offers comprehensive information on bed bug prevention, identification, and treatment.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Provides detailed guidance on bed bug biology, signs of infestation, and health-related concerns.
- National Pest Management Association (NPMA) – A valuable resource for understanding where bed bugs hide and how to inspect for them.
By staying informed and proactive, you can effectively manage and prevent bed bug infestations. Your home can remain a safe and comfortable environment, free from these unwelcome pests.




