Introduction
In recent years, the global resurgence of bed bugs has not only disturbed our peaceful nights but also sparked numerous discussions around these tiny invaders. While their presence is unmistakably unsettling, understanding their feeding habits is crucial to effectively tackling the issue. As you navigate the modern bed bug conundrum, knowledge is your best tool. These mostly nocturnal critters, known for their elusive nature, often raise a pressing question: How often do bed bugs feed?
By delving deep into the life and habits of bed bugs, we aim to equip you with invaluable insights. This complete guide is crafted to shed light on the intricate behaviors of bed bugs and provide you with actionable strategies to reclaim your home’s tranquility.
How Did Bed Bugs Get Their Name?
The name “bed bug” might seem quite straightforward, but there’s a fascinating history behind it. These pests have been a bane to humans for centuries, often hiding in bedding and mattresses, hence the term “bed” in their name.
The word “bug” historically refers to insects that suck blood, making it a fitting descriptor for these nighttime feeders. Bed bugs are incredibly adept at hiding near where their primary food source, which is human blood, rests – our beds. Over time, as people noticed these pests predominantly in their sleeping quarters, the name naturally evolved to highlight their favorite haunt.
Understanding Bed Bugs:
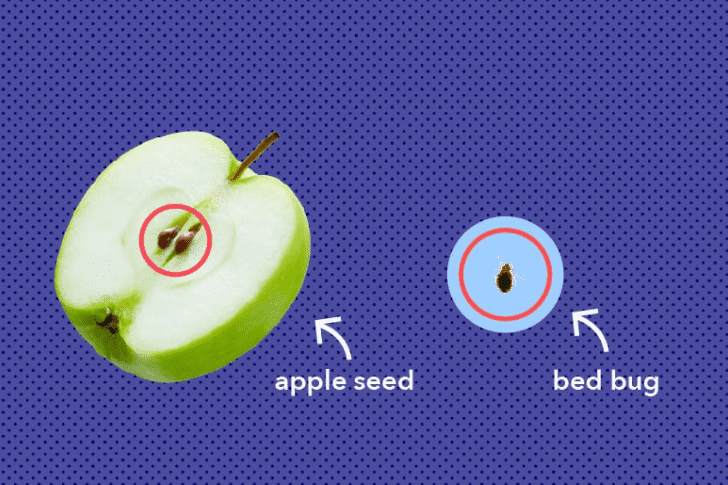
Bed bugs, those pests often hidden in the crevices of our homes, have coexisted with humans for centuries. Yet, how much do we truly know about them? Scientifically known as Cimex lectularius. These reddish-brown insects are roughly the size of an apple seed, making them easily overlooked until their population explodes.
Their life is characterized by three primary stages: eggs, nymphs, and adults. Beginning as minuscule, translucent eggs, bed bugs undergo a series of molts, gradually maturing into the bothersome adults that are notorious for disrupting our sleep.
While their appearance may suggest simplicity, understanding the lifecycle of bed bugs is a fundamental step towards mastering the methods to counteract their proliferation effectively.
Frequency of Bed Bug Feeding
One of the most unsettling characteristics of bed bugs is their reliance on human blood as their primary food source. But exactly how often do these pests seek out a meal? Bed bugs are chiefly nocturnal, coming out from their hiding spots under the shroud of darkness. These twilight forays are typically dictated by two main factors: the proximity of a host and the stage of their life cycle.
While nymphs, or juvenile bed bugs, may seek a blood meal every 3-7 days to support their growth, adults can sometimes go longer between feeds, depending on environmental conditions and food availability. However, it’s vital to note that several factors, such as room temperature and humidity, can influence these intervals. Knowledge of their feeding patterns not only helps in detecting their presence but also plays a pivotal role in devising effective extermination strategies.
While their preferred time to feed is usually an hour or two before dawn, they’re not strictly bound by this schedule. If conditions are right—like in a dimly lit room during the day—they might seize the opportunity to feed. However, their stealthy nature drives them to feed when their hosts, be it humans or animals, are in a deep state of rest. This reduces the chance of detection and disturbance. It makes complete sense. Interestingly, even though they can go for several months without a meal, regular feeding ensures their healthy reproduction and growth.
How Long Can Bed Bugs Go Without Feeding?
The resilience of bed bugs is often a subject of curiosity and concern. One of the remarkable aspects of these tiny pests is their ability to endure long periods without feeding. On average, bed bugs can go without a blood meal for several weeks to a few months, depending on factors like temperature and their life stage.
Nymphs, or young bed bugs, generally need to feed more frequently to mature into adulthood, yet they can still survive for several weeks without a meal. Adult bed bugs, on the other hand, display an astounding level of persistence. In cooler environments, where their metabolism slows down, they’ve been known to go without feeding for as long as a year.
This incredible survival tactic is part of what makes bed bug infestations particularly challenging to eradicate. Their ability to lie dormant means that even if you think they’ve disappeared, they could just be biding their time, waiting for the right moment to re-emerge, and feed. Hence, it’s crucial to be thorough and persistent in any bed bug elimination efforts.
The Aftermath of a Feed
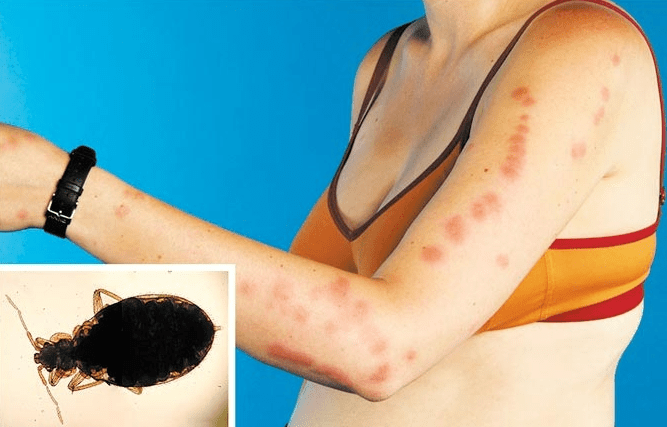
Waking up with a row of itchy, red welts is often the first tell-tale sign that bed bugs have paid a visit. But how can one be certain? Recognizing the symptoms of bed bug bites is fundamental in early detection and intervention. Unlike mosquito or flea bites, bed bug bites often appear in a linear or zig-zag pattern, sometimes grouped together.
They may initially present as small, flat, or slightly raised areas, becoming red, swollen, and increasingly itchy over time. While these are the general reactions, it’s essential to remember that not everyone responds to bed bug bites the same way. Some might have minimal signs, while others could exhibit more pronounced symptoms.
Distinguishing between bed bug bites and those from other insects is a critical step in confirming their presence, allowing you to act promptly and mitigate further infestations.
Can You Feel Bed Bug Bites?
One common misconception is that bed bugs are so tiny, you wouldn’t feel them biting. However, the reality is a tad more nuanced. While bed bugs are indeed stealthy feeders, the sensation of their bite can vary among individuals. Most people don’t feel the actual bite because bed bugs inject a small amount of anesthetic when they pierce the skin, ensuring their feeding goes unnoticed.
This clever tactic allows them to dine undisturbed. However, the aftermath is a different story. Within hours or sometimes days, the site of the bite can become red, itchy, and inflamed due to an allergic reaction to the proteins in the bed bug’s saliva. For some, the reactions are mild, while others experience intense itching and discomfort.
It’s worth noting that a few individuals might not exhibit any visible signs at all, making it even more challenging to detect a bed bug presence. Therefore, while the act of biting might go unfelt, the subsequent itchiness and skin irritations serve as telltale indicators of these unwelcome nocturnal guests.
Bed Bug Myths Busted
In our quest to understand and tackle bed bugs, it’s easy to stumble upon various myths that cloud our judgment. Clarifying these misconceptions is pivotal to formulating a successful eradication strategy. One prevalent myth is that bed bugs can only survive by feeding for extended durations.
In reality, a bed bug typically completes its meal within 5-10 minutes. Another widely held belief is that bed bugs only emerge in the dark. While they predominantly exhibit nocturnal behavior, bed bugs can and will feed during the day, especially if they’re hungry and a host is available. Busting these myths is more than just an exercise in truth; it’s about equipping ourselves with accurate information, steering clear of pitfalls, and optimizing our approach to deal with these persistent pests.
Prevention & Control
Defeating bed bugs is not just about reacting to their presence; proactive measures play an equally vital role. Early detection is the cornerstone of preventing full-blown infestations. But what signs should you be on the lookout for? Beyond the evident bite marks, subtle indications like dark fecal spots on sheets, tiny eggshells, or the distinct musty odor can signal a lurking bed bug issue. For a proactive approach, consider using bed bug interceptors, tools designed to trap these critters trying to climb up your bed legs.
When it comes to remedies, while there are DIY home solutions that can offer temporary relief, for severe infestations, professional intervention becomes necessary. Integrating both prevention techniques and effective remedies, you’re arming yourself with a two-pronged approach, ensuring a bed bug-free environment.
Understanding Hunger: Can Bed Bugs Starve?
Bed bugs, for all their nuisance, are surprisingly resilient creatures, often leading many to wonder about their survival tactics in the absence of a regular blood meal. So, how long can these pests truly endure without feeding? Remarkably, under optimal conditions, adult bed bugs can live for several months without a meal.
This stark fact emphasizes their hardiness and the challenges involved in eradicating an infestation completely. Their younger counterparts, the nymphs, however, have a shorter fasting threshold. They need more frequently to progress through their growth stages.
In Summary
The journey through the world of bed bugs has undoubtedly been enlightening. We shed light on their behaviors, habits, and the myths surrounding them. As we’ve explored, understanding their lifecycle, feeding patterns, and resilience is more than just an educational endeavor. It’s a proactive strategy to regain control over our living spaces.
Early detection, paired with informed and rigorous eradication methods, is our most potent weapon against these unwelcome guests. Stay vigilant, continuously educate yourself, and prioritize consistent preventive measures. Together, we can turn the tide against bed bugs, ensuring restful nights and peace of mind.