Introduction
Bed bug bites are a common issue that many people face. Understanding the duration of these bites is crucial for proper treatment and relief. Bed bugs are small, elusive insects that feed on human blood, often resulting in itchy, red welts on the skin. Knowing how long bed bug bites last helps in managing symptoms and reducing discomfort.
Typically, bed bug bites appear in clusters or lines and can be confused with other insect bites. It’s essential to correctly identify bites to ensure effective treatment. Immediate symptoms often include itching, redness, and slight swelling, which can vary in severity from person to person.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how long bed bug bites last, the stages of healing, and effective treatment options. We will also provide tips on preventing future bites and understanding bed bug behavior. For more detailed information on bed bug infestations and their management, visit CDC’s Bed Bug Information.
By the end of this post, you will have a clear understanding of how to handle bed bug bites and prevent them from recurring. Let’s delve into the details to help you manage and alleviate the discomfort caused by these persistent pests. …Click Here to Read More Fascinating Bed Bug Articles!
What Are Bed Bug Bites?
Bed bug bites are the result of bed bugs feeding on human blood. These small, nocturnal insects are skilled at hiding in cracks and crevices, making them difficult to detect. Bed bug bites often cause itchy, red welts on the skin, leading to significant discomfort.
Identifying Bed Bug Bites
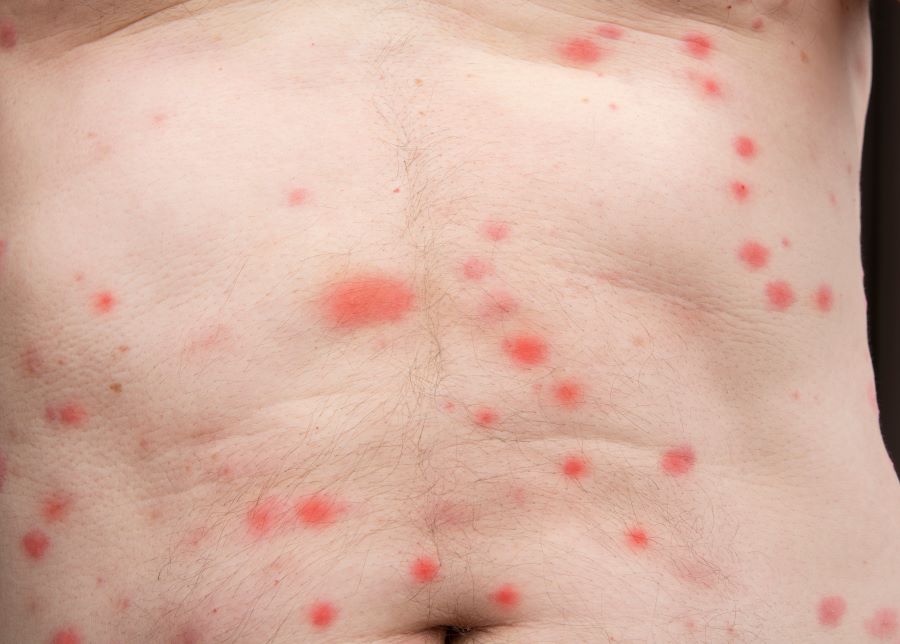
To accurately identify bed bug bites, look for specific patterns. Bed bug bites usually appear in clusters or lines, as the bugs tend to feed in a linear fashion. Common areas for bites include the arms, shoulders, and legs. Unlike mosquito bites, these do not have a centralized red bump.
Common Symptoms and Reactions
Bed bug bites can cause various symptoms, including:
- Redness: The bitten area often turns red.
- Itching: Bed bug bites are notoriously itchy.
- Swelling: Some people may experience mild swelling around the bite.
- Blistering: In severe cases, bites may blister.
How Bed Bug Bites Differ from Other Insect Bites
Differentiating bed bug bites from other insect bites is crucial for proper treatment. Here are some key differences:
- Mosquito Bites: These typically have a centralized bump and can appear randomly on the body.
- Flea Bites: Flea bites are usually smaller and concentrated around the ankles and lower legs.
- Spider Bites: Spider bites are often isolated and can be more painful, sometimes with a central puncture mark.
Accurate identification of bed bug bites is the first step toward effective treatment and management. For additional insights on identifying insect bites, check out Mayo Clinic’s Guide on Insect Bites.
Understanding what bites are and how they differ from other bites can help you take the necessary steps to alleviate symptoms and prevent further bites.
Initial Reaction to Bed Bug Bites
When bed bugs bite, the initial reaction varies from person to person. Understanding these immediate symptoms helps in early identification and treatment. These typically cause itching, redness, and mild swelling, which can be quite uncomfortable.
Immediate Symptoms Upon Being Bitten
As soon as a bed bug bites, the body’s immune system reacts to the insect’s saliva. This reaction usually manifests within a few hours to a day after the bite. Common immediate symptoms include:
- Red Bumps: Small, red bumps appear at the site of the bite.
- Itching: Intense itching often accompanies these bumps.
- Swelling: Mild swelling around the bite area is common.
- Pain: Some individuals may experience a slight burning sensation.
Physical and Allergic Reactions
The body’s reaction to bed bug bites can range from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s sensitivity. Common reactions include:
- Local Reactions: Most people will have localized reactions such as redness, swelling, and itching.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may have severe allergic reactions, including hives, blisters, or difficulty breathing. These reactions require immediate medical attention.
- Secondary Infections: Excessive scratching can lead to secondary skin infections. Keeping the area clean and avoiding scratching can prevent this.
Common Areas of the Body Affected
Bed bugs tend to bite exposed skin, making certain areas more prone to bites. These areas include:
- Arms: Particularly the forearms and upper arms.
- Shoulders: The upper back and shoulders are common bite sites.
- Legs: Bites often appear on the thighs and lower legs.
- Face and Neck: Bed bugs can also bite the face and neck, especially if these areas are exposed during sleep.
Recognizing these immediate reactions to bed bug bites is crucial for prompt treatment and relief. For more information on managing allergic reactions to insect bites, visit WebMD’s Guide on Insect Bites.
Early identification and understanding of the initial reactions to bed bug bites can significantly reduce discomfort and prevent further complications. Taking appropriate measures as soon as you notice these symptoms is essential for effective treatment.
Duration of Bed Bug Bites
The duration of bed bug bites varies depending on several factors. Understanding how long these bites last helps manage symptoms and determine when to seek medical attention. Generally, bed bug bites can last from a few days to several weeks.
Typical Time Frame for Bed Bug Bites to Heal
Most bed bug bites heal within one to two weeks. The initial redness and itching usually subside within a few days. However, in some cases, the itching and marks can persist for up to two weeks or longer.
Factors Influencing the Duration of Bites
Several factors can affect how long bed bug bites last, including:
- Individual Immune Response: People with stronger immune responses may experience longer-lasting symptoms.
- Severity of the Infestation: Frequent bites from a severe infestation can prolong healing time.
- Frequency of Bites: Repeated bites in the same area can cause prolonged irritation and slower healing.
Individual Immune Response
The body’s immune response plays a significant role in the duration of bed bug bites. Some people may have a mild reaction with quick healing, while others might experience prolonged symptoms due to a more vigorous immune response. Factors such as age, overall health, and sensitivity to insect bites can influence the immune response.
Severity of the Infestation
A severe bed bug infestation often results in more frequent bites. This repeated exposure can lead to prolonged symptoms and slower healing. Managing the infestation is crucial for reducing the frequency and severity of bites.
Frequency of Bites
When bed bugs bite the same area repeatedly, the skin may become more irritated and take longer to heal. Continuous scratching of the affected area can also lead to secondary infections, further prolonging the healing process.
Understanding these factors can help in managing and reducing the duration of bed bug bites. For more information on the factors affecting insect bite reactions, visit Healthline’s Guide on Insect Bites.
Knowing the typical duration and factors influencing bed bug bites enables effective treatment and symptom management, ensuring quicker relief and recovery.
Stages of Bed Bug Bite Healing
Understanding the stages of bed bug bite healing can help manage symptoms and apply appropriate treatments. The healing process typically progresses through three main stages: early, middle, and late.
Early Stage: Redness and Itching
In the early stage, bed bug bites appear as red, itchy welts. This stage occurs within a few hours to a day after being bitten. Symptoms include:
- Red Bumps: Small, red, raised bumps at the bite sites.
- Intense Itching: Significant itching around the bite areas.
- Mild Swelling: Slight swelling may accompany the redness and itching.
Middle Stage: Swelling and Blistering
As the bites continue to heal, they may enter the middle stage, which involves more pronounced symptoms:
- Increased Swelling: The area around the bites may swell more.
- Blister Formation: In some cases, small blisters can form on the bites.
- Persistent Itching: Itching remains intense and may lead to scratching, which should be avoided to prevent infection.
Late Stage: Scabbing and Fading Marks
In the late stage, bed bug bites begin to heal completely:
- Scabbing: The bites may scab over as they heal.
- Reduced Itching: Itching decreases as the bites start to fade.
- Fading Marks: Redness and swelling diminish, and the skin returns to normal.
Managing Symptoms Through Each Stage
Proper management of bed bug bites through each stage can reduce discomfort and promote faster healing. Here are some tips for each stage:
- Early Stage: Apply a cold compress to reduce itching and swelling. Use topical antihistamines or hydrocortisone creams to relieve itching.
- Middle Stage: Keep the area clean and avoid scratching. Apply antiseptic creams to prevent infection if blisters form.
- Late Stage: Continue using soothing creams if itching persists. Moisturize the skin to help with healing and reduce scarring.
Understanding the stages of bed bug bite healing is crucial for effective symptom management. For more detailed guidance on treating insect bites, visit Mayo Clinic’s Insect Bite Care.
By recognizing and managing the stages of bed bug bite healing, you can alleviate symptoms more effectively and ensure a quicker recovery.
Preventing Bed Bug Bites
Preventing bed bug bites is essential for maintaining comfort and health. Implementing effective prevention strategies can help avoid infestations and reduce the risk of bites. Here, we outline tips for avoiding bed bugs, protecting yourself while traveling, and steps to take at home.
Tips for Avoiding Bed Bug Infestations
Preventing an infestation begins with vigilance and proactive measures. Follow these tips to keep bed bugs at bay:
- Inspect Second-Hand Furniture: Thoroughly check any second-hand furniture for signs of bed bugs before bringing it into your home.
- Reduce Clutter: Minimize clutter in your living spaces to reduce hiding spots for bed bugs.
- Seal Cracks and Crevices: Seal any cracks and crevices in walls and furniture where bed bugs might hide.
- Use Protective Covers: Encase mattresses and box springs in protective covers designed to prevent bed bug infestations.
Effective Methods to Protect Yourself While Traveling
Traveling can increase the risk of encountering bed bugs. Protect yourself by following these guidelines:
- Inspect Hotel Rooms: Upon arrival, inspect the hotel room for signs of bed bugs, including the mattress, headboard, and furniture.
- Keep Luggage Elevated: Store luggage on a luggage rack away from the bed and walls.
- Use Luggage Liners: Consider using luggage liners to add an extra layer of protection against bed bugs.
- Wash and Dry Clothing: After returning home, wash and dry all clothing on high heat to kill any potential bed bugs.
Steps to Take in Your Home to Prevent Bites
Maintaining a clean and well-monitored home environment is crucial for preventing bed bug bites. Implement these steps to protect your home:
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum and clean your home regularly, paying special attention to areas around the bed and furniture.
- Monitor for Signs: Regularly check for signs of bed bugs, such as small rust-colored stains or tiny, dark spots.
- Isolate Infested Items: If you suspect an infestation, isolate infested items by placing them in sealed plastic bags until they can be treated.
- Seek Professional Help: If you discover bed bugs, contact a professional pest control service for effective treatment and eradication.
For more information on preventing bed bug infestations, visit EPA’s Bed Bug Prevention Tips.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug bites and ensure a comfortable living environment.
Understanding Bed Bug Behavior
Understanding the behavior of bed bugs is essential for effective prevention and control. Knowing their life cycle, feeding habits, and how they spread can help you take proactive measures to protect your home.
Bed Bug Life Cycle
The bed bug life cycle consists of several stages, from egg to adult. Each stage is crucial in understanding their behavior and managing infestations.
- Eggs: Female bed bugs lay tiny, white eggs in hidden crevices. These eggs hatch within 6 to 10 days.
- Nymphs: After hatching, bed bugs go through five nymphal stages, shedding their exoskeleton after each stage. Nymphs require a blood meal to molt and grow.
- Adults: Adult bed bugs are reddish-brown and about the size of an apple seed. They can live for several months, feeding regularly on blood.
Feeding Habits
Bed bugs are nocturnal feeders, preferring to feed on human blood while their hosts are asleep. Understanding their feeding habits can help in identifying and managing infestations.
- Feeding Time: Bed bugs typically feed at night, usually just before dawn. However, they can adapt to their host’s sleeping patterns and feed at any time.
- Feeding Frequency: Bed bugs feed every 5 to 10 days. Each feeding session lasts about 5 to 10 minutes.
- Feeding Sites: They prefer exposed skin, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands. Bites often appear in clusters or lines due to their feeding pattern.
How Bed Bugs Spread and Infest Homes
Bed bugs are adept at spreading and infesting new environments. Understanding their methods of travel and infestation can help prevent their spread.
- Hitchhiking: Bed bugs often spread by hitching rides on clothing, luggage, furniture, and other personal belongings. This makes them a common issue in hotels, public transportation, and shared living spaces.
- Crawling: Bed bugs can crawl significant distances to find new hiding spots. They can move between rooms and even different floors of a building.
- Rapid Reproduction: A single female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs in her lifetime, leading to rapid infestations if not promptly managed.
Recognizing Signs of a Bed Bug Infestation
Early detection of bed bug infestations is crucial for effective management. Here are some common signs to look for:
- Bite Marks: Itchy, red welts on your skin, especially in a linear or clustered pattern, can indicate bed bug bites.
- Fecal Spots: Small, dark spots on bedding, mattresses, and furniture are bed bug feces.
- Shed Skins: As bed bugs grow, they shed their exoskeletons. These discarded skins are often found near their hiding spots.
- Eggshells: Tiny, white eggshells in cracks and crevices can indicate an infestation.
- Live Bugs: Seeing live bed bugs, especially in hiding spots like mattress seams, bed frames, and behind picture frames, confirms an infestation.
Understanding bed bug behavior is key to preventing and managing infestations. For more detailed information on bed bug behavior and control, visit National Pest Management Association’s Bed Bug Guide.
By gaining insights into their life cycle, feeding habits, and methods of spread, you can take effective steps to protect your home from bed bugs.
Conclusion
Understanding the duration of bed bug bites and how to treat them is crucial for managing discomfort and preventing further issues. Bed bug bites can cause significant discomfort, but with the right knowledge and actions, you can effectively manage and alleviate symptoms. By identifying bed bug bites early, recognizing the stages of healing, and applying appropriate treatments, you can ensure a quicker recovery.
Recap of Key Points
- Identification: Bed bug bites typically appear in clusters or lines and cause itching, redness, and mild swelling.
- Healing Stages: The healing process includes stages of redness and itching, swelling and blistering, and scabbing and fading marks.
- Treatment: Effective treatments include immediate first aid, over-the-counter remedies, and home remedies. Seek medical attention for severe reactions or persistent symptoms.
- Prevention: Preventing bed bug bites involves inspecting second-hand furniture, reducing clutter, sealing cracks, and using protective covers. Travel precautions and regular home maintenance are also essential.
Encouragement to Seek Professional Help
If you suspect a bed bug infestation or if symptoms persist, seeking professional help is vital. Professional pest control services can effectively identify and eliminate bed bug infestations, ensuring your home is safe and comfortable.
Final Tips for Dealing with Bed Bug Bites and Preventing Future Infestations
- Stay Vigilant: Regularly inspect your home and surroundings for signs of bed bugs.
- Implement Prevention Strategies: Follow the outlined prevention tips to avoid infestations and reduce the risk of bites.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about bed bug behavior and management techniques to better protect yourself and your home.
Additional Resources
For more detailed information and resources on bed bug bites and prevention, consider visiting the following links:
- CDC’s Bed Bug Information: Comprehensive guide on bed bug biology, prevention, and management.
- Mayo Clinic’s Guide on Insect Bites: Detailed information on identifying and treating insect bites.
- EPA’s Bed Bug Prevention Tips: Practical advice on preventing bed bug infestations.
By following these guidelines and utilizing available resources, you can effectively manage bed bug bites and prevent future infestations, ensuring a healthier and more comfortable living environment.




