When Do Bed Bugs Lay Eggs?
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration into the reproductive habits of one of the most persistent household pests: bed bugs. Understanding the intricacies of bed bug life cycles is more than academic knowledge. It’s a crucial weapon in the battle against infestations. These tiny invaders operate on a schedule dictated by nature. And by delving into when bed bugs lay eggs, we arm ourselves with the power to preempt and dismantle their breeding grounds, turning the tide in our favor.
Bed bugs, known scientifically as Cimex lectularius, lead secretive lives and are masters of evasion. Their life cycle encompasses several stages. Starting as an egg no larger than a speck of dust and culminating in the adult bed bug. A creature synonymous with sleepless nights and itchy, unwelcome bites. Each phase of their development plays a pivotal role in the proliferation of their population. And at the heart of their survival strategy lies their egg-laying habits. It is at this initial stage that intervention is most effective. Making our discussion not just informative but vital for those seeking respite from these nocturnal nuisances.
Let’s Get into It
As we peel back the layers of the bed bug’s secretive world. Our journey will reveal not just when these pests lay their eggs, but how they’ve adapted to ensure their offspring survive and thrive. Stay tuned as we uncover the tell-tale signs of bed bug egg-laying. Explore optimal conditions that invite these pests into our homes, and ultimately provide you with the knowledge to stop an infestation in its tracks.
In concert with our insights, we’ll reference authoritative sources such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Understanding and Controlling Bed Bugs, which underscores the importance of identifying and targeting bed bugs at every stage of their life cycle. By aligning our expertise with validated research, we’re not just sharing knowledge. We’re equipping you with the tools for effective pest management.
With our guide, you’ll navigate through the complexities of bed bug infestations with confidence. Let’s embark on this educational journey together. Turning the page on bed bugs and reclaiming the peace and comfort of our living spaces.
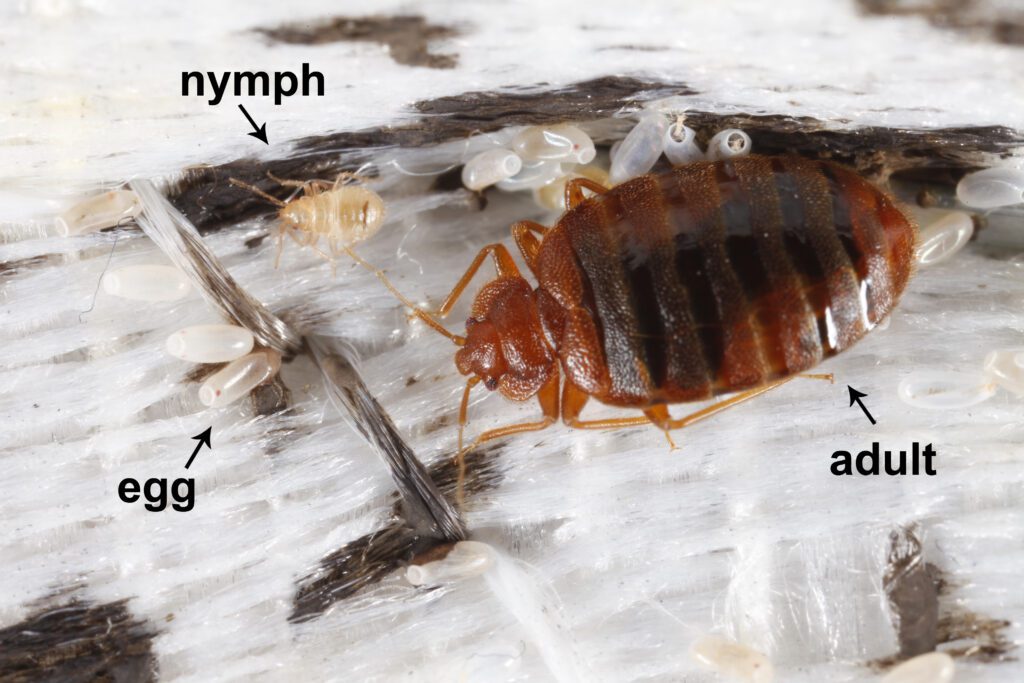
Embarking further into the bed bug’s enigmatic existence, we encounter their life cycle. An intricate series of transformations that bed bugs undergo from their inception as eggs to their final form as reproductive adults. This life cycle is divided into five stages after hatching. The nymph stages, each requiring a blood meal to molt and progress to the next level. As these stages unfold, the duration and conditions under which they develop become critical in managing and preventing an infestation.
Understanding the Stages: From Egg to Adult
The genesis of a bed bug’s life starts with an egg. These eggs are pearl-white, measuring about 1mm in length, making them challenging to detect without a keen eye. After approximately 6-10 days, a nymph emerges. These nymphs, miniature and translucent versions of their adult counterparts, will pass through five molts before reaching maturity. A process that can take anywhere from five weeks to four months, influenced heavily by temperature and access to food.
The Nymphal Stages: Growth Spurts of Bed Bugs
Throughout the nymphal stages, bed bugs are voracious feeders, each blood meal marking a transition closer to adulthood. They undergo a series of molts, shedding their exoskeleton, a clear sign of their presence.
With each molt, the nymphs grow larger, and their color darkens, indicating their approaching maturity. Bed bug nymphs require approximately one week for each instar stage, provided they have consistent access to blood meals. In colder climates or when a food source is scarce, these stages can be prolonged, extending the timeline of development significantly.
Maturation: When Nymphs Become Breeders
As the nymphs navigate through their growth, they eventually mature into adult bed bugs. Adults are about the size of an apple seed, brownish in color, and once they reach this stage, reproduction becomes their sole focus. The life expectancy of a mature bed bug ranges from four to six months. Although under optimal conditions, they can live for over a year. During this time, a female bed bug is capable of laying hundreds of eggs. Given the right conditions, perpetuating the cycle of infestation.

This understanding of the bed bug life cycle is not just a lesson in biology—it’s a blueprint for intervention. By targeting specific stages, particularly before and during the nymph phases, we can implement control methods that are both timely and effective. According to research from the University of Minnesota Let’s Beat the Bed Bug! interrupting the life cycle is key to managing these pests. By addressing the bed bug’s developmental timeline, we’re setting the stage for not only addressing current infestations but also for establishing preventative measures to safeguard our homes from future intrusion.
Delving deeper into the reproductive nuances of bed bugs, we reach the pivotal moment that precedes egg-laying: the mating ritual. Understanding this critical precursor is essential, for it is through this process that the cycle of infestation perpetuates. Bed bug mating behaviors are unique among pests. And grasping the mechanics provides us with the insight necessary to target interventions more effectively.
The Unique Mating Process of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs employ a mating process known as “traumatic insemination.” Unlike most creatures, the male bed bug bypasses the traditional reproductive organs of the female. Instead piercing her abdomen to deposit sperm directly into her body cavity. This method is as harsh as it sounds, and it can take a toll on the female’s health and longevity. The implications of this unusual mating technique are twofold. Females often try to escape it by moving away from male-dominated areas. And they may lay eggs in these new locations, potentially spreading the infestation.
Female Bed Bugs: Bearing the Brunt of Reproduction
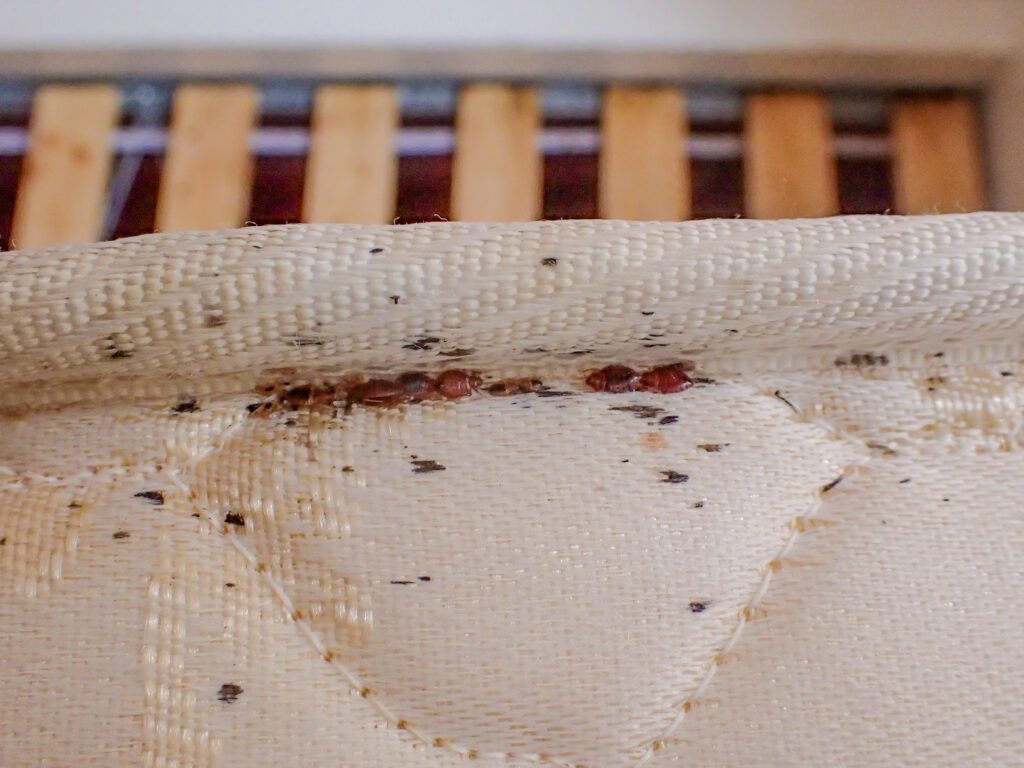
After enduring the traumatic insemination process, female bed bugs are responsible for the next generation. A female is capable of laying one to five eggs each day, amounting to up to 500 over her lifetime. These eggs are cemented in hidden crevices, away from potential threats, ensuring the survival of her offspring. The frequency and quantity of egg-laying are contingent upon adequate feeding opportunities and the overall health of the female. Directly linking the severity of an infestation to the availability of blood meals.
Mating Frequency: A Factor in Egg Production
The frequency of mating also plays a crucial role in the number of eggs a female bed bug can produce. While a male can mate with multiple females, a female needs time to recover after the invasive mating process before she can lay viable eggs. Excessive mating can reduce her lifespan and egg-laying potential, affecting the population dynamics within an infested area.
Recognizing the signs of mating and understanding its consequences is vital for controlling the spread of bed bugs. By interrupting this process, whether through chemical treatments that deter males or by isolating females. We can significantly reduce the rate at which new bed bugs are born. The University of Kentucky’s entomology department provides in-depth insights into these behaviors in their publication Bed Bug Biology and Control underscoring the importance of mating patterns in bed bug management strategies. By targeting the heart of reproduction, we strike a critical blow to the bed bug’s lifecycle and carve a path toward a bed bug-free environment.
As we venture further into the world of bed bugs, we arrive at the environmental factors that serve as the backdrop for their reproductive success. Like all creatures, bed bugs are at the mercy of their surroundings. With certain conditions proving more favorable for their proliferation. By identifying and manipulating these conditions, we can create strong deterrents against the laying of bed bug eggs. Significantly hindering the growth of their population.
The Ideal Environment for Bed Bug Reproduction
Bed bugs are not simply passive inhabitants of our homes. They are active seekers of the optimal conditions for their survival and reproduction. Temperature and humidity play significant roles in this quest. These pests thrive in temperatures between 70°F and 90°F (21°C to 32°C), which, unfortunately for us, are conditions common in many inhabited spaces. High humidity levels also facilitate more successful egg-laying and hatching rates. Conversely, temperatures that are too low or too high can disrupt bed bug mating and egg production, potentially serving as a natural form of pest control.
How Access to Food Influences Egg-Laying

A blood meal is the cornerstone of bed bug survival and the catalyst for their reproductive process. Female bed bugs require a consistent food source to produce eggs, as the act of feeding stimulates egg development. After feeding, a female bed bug can lay several eggs per day for several days. The proximity of their host—us—thus directly affects their ability to reproduce. It is this reliance on blood meals that can be exploited; by strategically applying insecticides or utilizing mattress encasements, we can cut off their food supply, thereby reducing the chances of a female laying eggs.
Bed Bug Egg-Laying: A Synchronized Activity
Interestingly, bed bug egg-laying is not a sporadic event but a synchronized activity. It’s closely aligned with their feeding cycle, with females often seeking secluded and protected areas shortly after a meal to lay their eggs. This behavior suggests a strategic approach to ensuring the maximum survival rate for their offspring, and it also provides us with an opportunity for intervention. By understanding this synchronization, we can predict and target potential egg-laying sites, disrupting the cycle.
Acknowledging these factors that influence where and when bed bugs lay their eggs allows for a proactive approach to control and prevention. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) emphasizes in their comprehensive guide Integrated Pest Management in Schools the necessity of creating environments inhospitable to pests as a cornerstone of effective management. By manipulating temperature, humidity, and access to a host, we can create a less inviting space for bed bugs, thereby controlling their ability to lay eggs and expand their numbers. With the right knowledge and tactics, we can maintain a living space that discourages bed bugs from settling in and calling it home.
Continuing our comprehensive exploration of bed bug biology, it’s critical to highlight the signs and indicators of egg-laying activity within our living spaces. Early detection of these signs can be the difference between a manageable situation and a full-blown infestation. Armed with this knowledge, we can implement timely measures to disrupt the reproductive cycle of these elusive pests and protect our homes.
Indicators of Bed Bug Egg-Laying
The most direct evidence of bed bug reproduction is the sighting of the eggs themselves. These tiny, pearl-like capsules are often tucked away in the seams of mattresses, within the cracks of furniture, or behind wall fixtures. Spotting these eggs, which are about the size of a speck of dust, requires vigilance and sometimes a magnifying glass. Another tell-tale sign is the discovery of eggshells and exoskeletons, which bed bug nymphs leave behind as they grow. These remnants are lighter in color and, like the eggs, are often hidden in discrete locations.
Recognizing Bed Bug Habitats
Bed bugs are masters of concealment, choosing to lay their eggs in areas that provide safety and proximity to a food source. This means checking places that offer warmth, darkness, and isolation, such as behind headboards, inside electrical outlets, and even within personal belongings. These locations are strategically chosen to give the nymphs immediate access to food upon hatching, emphasizing the need for thorough inspections and targeted treatments in these areas.
Preventative Measures: Warding Off Egg-Laying Bed Bugs
Prevention is invariably the most effective strategy in the war against bed bugs. This involves regular cleaning and vacuuming of potential hiding spots, using protective encasements on mattresses and pillows, and reducing clutter where bed bugs can hide and lay eggs. For those traveling, inspecting hotel rooms and luggage is crucial to prevent inadvertently transporting bed bugs back home.
Detecting and responding to the presence of bed bug eggs requires a blend of keen observation and preemptive action. According to a guide from the National Pest Management Association NPMA’s Best Practices for Bed Bug Management, understanding the bed bug’s habits, including where and when they lay their eggs, is paramount for effective pest management. By staying vigilant and employing a comprehensive prevention strategy, we can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug infestations and safeguard our living spaces from these unwelcome guests.
Addressing a bed bug infestation requires a strategic and multi-faceted approach, especially when tackling the core issue of egg-laying. By interrupting the life cycle of bed bugs at the egg stage, we can prevent a new generation from maturing and reproducing, thereby breaking the chain of infestation. Let’s explore the most effective methods to eradicate bed bug eggs and halt their proliferation in our homes.
Targeted Chemical Treatments
Insecticides remain a primary weapon in our arsenal against bed bugs. Products containing ingredients like pyrethroids, desiccants, or insect growth regulators are designed to penetrate the bed bugs’ hideouts and neutralize the eggs. However, these chemicals must be used judiciously and often in combination with other methods, as bed bugs can develop resistance to certain compounds. It’s imperative to select EPA-registered insecticides and to follow the label instructions meticulously to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Non-Chemical Controls: Heat and Freezing Treatments
Bed bug eggs are vulnerable to extreme temperatures. Heat treatments, which involve raising the temperature of the affected area to a level lethal to bed bugs and their eggs, can be remarkably effective. Similarly, freezing infested items at temperatures below 0°F (-18°C) for at least four days can destroy eggs. These non-chemical treatments can be particularly appealing for those seeking a more environmentally friendly approach or when dealing with areas where chemical sensitivity is a concern.
Professional Intervention and Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Due to the complexity of bed bug life cycles and the difficulty in eliminating eggs, professional pest control services are often the most reliable solution. Professionals employ an Integrated Pest Management approach, combining thorough inspections, treatments (chemical and non-chemical), and follow-up evaluations. This systematic and tailored strategy ensures that not only are the bed bugs and their eggs addressed but also that preventive measures are put in place to avoid future infestations.
Eradicating bed bug eggs is a critical step in managing an infestation. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlight the importance of combining various treatment methods to tackle bed bug populations effectively. By incorporating these practices, we stand the best chance of not only dealing with the current problem but also of establishing a bed bug-resistant environment, thus protecting our homes and health in the long term.
In conclusion, confronting the challenge of bed bugs and their eggs requires a comprehensive understanding and proactive approach. From recognizing the signs of egg-laying to implementing targeted eradication measures, each step is crucial in maintaining a bed bug-free environment. Let’s recap the key takeaways and provide additional resources for those seeking further assistance in their battle against bed bugs.
Key Takeaways for Effective Bed Bug Egg Management
- Vigilance is Vital: Regular inspection and early detection of bed bug eggs can prevent widespread infestations.
- Environmental Control: Manipulate temperatures and reduce clutter to create unfavorable conditions for bed bugs.
- Chemical and Non-Chemical Treatments: Use insecticides responsibly and consider heat or freezing treatments for a comprehensive approach.
- Professional Help: When in doubt, enlist pest control professionals who can provide a customized Integrated Pest Management plan.
By employing the strategies discussed, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of bed bug infestations. Remember, effective bed bug control is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Stay educated, stay prepared, and continue to leverage expert advice and resources to keep these persistent pests at bay. Through diligence and informed action, we can protect our homes, our health, and our peace of mind from the hidden threat of bed bugs and their eggs.