Introduction
If you’ve ever dealt with a bed bug infestation, you know how essential it is to understand the enemy you’re facing. What could be more crucial than understanding how these pests multiply and expand their colonies? Knowing the mechanisms behind bed bug reproduction can arm you with the strategies you need to eradicate them effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into every facet of bed bug reproduction—starting with what bed bugs are, to their complicated life cycle, mating behaviors, and even effective control methods. Equipped with this knowledge, you’ll be better prepared to break the cycle of infestation and reclaim your living space. So, How Do Bed Bugs Reproduce?
Why is this topic so critical? According to a study published in the Journal of Medical Entomology, bed bugs can lay up to five eggs per day and may lay nearly 500 eggs in a lifetime under optimal conditions [source]. Understanding the rapid rate of reproduction can alert you to the urgency of tackling the problem as quickly and thoroughly as possible.
With this in-depth post, our aim is to provide you a one-stop resource, researched and written, that answers all your questions about how bed bugs reproduce. Read on to learn more.
Bed Bug Basics: What Are Bed Bugs?
You’ve probably heard the old bedtime saying, “Don’t let the bed bugs bite.” But what exactly are bed bugs? Why are they such a significant concern? Bed bugs are small, brownish insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. Their flat bodies enable them to hide in tiny spaces, often in mattresses, bed frames, and even cracks in the wall. While they are primarily nocturnal, these pests can adapt to the sleeping patterns of their hosts, making them incredibly elusive.
Description and Characteristics
Adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed, with oval-shaped bodies that balloon after a blood meal. They lack wings, so they cannot fly, but their six-legged structure allows them to crawl quickly over surfaces. Young bed bugs, often referred to as nymphs, are smaller and almost translucent, becoming browner as they mature.
Where They Usually Live
Bed bugs are experts at finding hideouts close to their human hosts. While their name suggests they’re found mainly in beds, these pests can also dwell in furniture, carpets, and even electronic appliances. They’re common in hotels, dormitories, and apartment buildings—essentially anywhere that has a high turnover of temporary occupants.
Why They Are a Problem
Besides the itchy, red welts they cause, bed bugs can also lead to various psychological issues, including anxiety and insomnia. Their resilience and rapid rate of reproduction make them a challenging pest to eliminate. A study by the University of Kentucky entomologists found that bed bugs can survive up to five months without a blood meal under colder conditions [source].
By gaining a fundamental understanding of what bed bugs are, you’ll be better equipped to recognize and manage an infestation. In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the bed bug life cycle to explore how they reproduce, thereby arming you with knowledge that can make your eradication efforts more effective.
The Bed Bug Life Cycle: A Roadmap to Reproduction
To effectively combat a bed bug infestation, it’s crucial to comprehend their life cycle. Understanding the developmental stages that bed bugs go through can provide key insights into when they are most vulnerable and how they reproduce. This understanding is central to disrupting the cycle and implementing successful treatment strategies. So, let’s get into How Bed Bugs Reproduce?
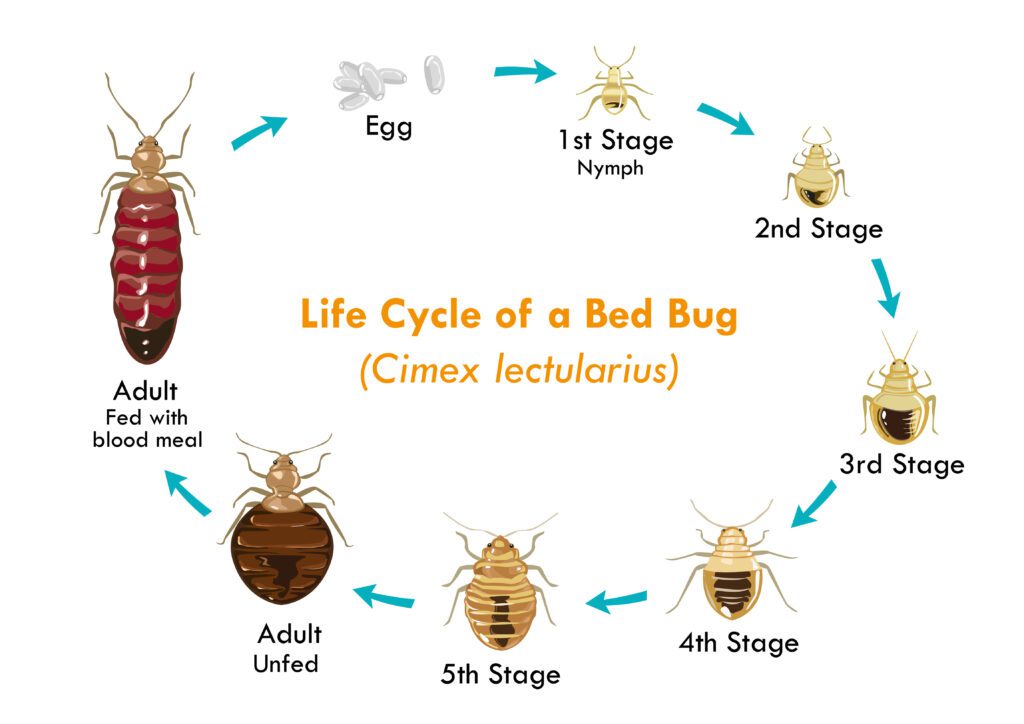
Eggs: The Beginning
Bed bugs start their life as tiny, milky-white eggs, usually about 1 mm in length. These eggs are often laid in secluded places, sticking to surfaces thanks to a glue-like substance. Within six to ten days, these eggs hatch to release nymphs, entering the first stage of their life.
Nymph Stages: Juvenile Phases
After hatching, the nymphs go through five developmental stages, requiring a blood meal at each stage to molt to the next. Nymphs look similar to adult bed bugs but are smaller and lighter in color. Each molting stage makes them darker and closer to the adult size. The entire nymph stage can last from three weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions and access to blood meals.
Adult Bed Bugs: The Reproductive Stage
Once they reach adulthood, bed bugs are ready for the reproductive phase of their life cycle. Female bed bugs can lay hundreds of eggs in their lifetime, especially when feeding is abundant.
Armed with this detailed understanding of the bed bug life cycle, you’re one step closer to devising an effective plan for eradication. In the sections that follow, we’ll discuss the intricacies of bed bug mating behavior and reproductive rates, so you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what you’re up against.
How Do Bed Bugs Reproduce?
When it comes to stopping a bed bug infestation, one of the key elements is disrupting their reproductive process. But to do that effectively, you must first understand how bed bug’s mate. Unlike many other insects, bed bugs have a unique and somewhat violent mating ritual, which has its own implications for their population growth and your extermination strategy.
Mating Behavior: The Traumatic Insemination Process
Bed bugs employ a method known as traumatic insemination. In this process, the male pierces the female’s abdomen with his specialized reproductive organ, bypassing the female’s reproductive tract to deposit sperm directly into her body cavity. This unique mating mechanism is efficient but can also lead to physical harm for the female bed bug, affecting her overall health and lifespan.
Frequency: How Often Do Bed Bugs Mate?
A common misconception is that bed bugs mate frequently. However, due to the traumatic nature of the process, females often try to avoid repeated mating by moving to different locations after laying eggs. Nonetheless, in environments with a high male-to-female ratio, frequent mating can occur, leading to increased stress and decreased lifespan for the females.
Potential Consequences of Mating: Female Exhaustion and Death
Frequent traumatic insemination can have serious consequences for female bed bugs, including shorter lifespans and reduced egg-laying capabilities. According to research from the University of Sheffield, this aggressive mating behavior can even lead to the death of female bed bugs [source].
Understanding the complexities of bed bug mating behavior offers another crucial angle in tackling infestations. Up next, we’ll look at the locations where female bed bugs prefer to lay their eggs, as this knowledge can serve as a linchpin in your efforts to control and eliminate these resilient pests.
Where Do Bed Bugs Lay Eggs?
Now that we have looked into How Do Bed Bugs Reproduce, let’s look at where they Lay Eggs. Knowing where to look is half the battle in any extermination effort. When it comes to bed bugs, locating their egg-laying sites can offer a significant advantage in disrupting the reproduction cycle and successfully eradicating an infestation. So, where do female bed bugs lay their eggs, and what do you need to know to find them?
Common Locations for Egg-Laying
Bed bugs prefer to lay their eggs in dark, hidden locations, often close to their feeding sites. Popular spots include the seams and folds of mattresses, the joints of bed frames, behind wallpapers, and even inside electrical outlets. In more severe infestations, they may venture farther away from the bed to lay eggs, making them harder to locate and eliminate.
Identifying Bed Bug Eggs
Bed bug eggs are tiny, about the size of a pinhead, and have a pearlescent, milky-white appearance. Their small size and coloration make them difficult to spot with the naked eye, but a flashlight and a magnifying glass can aid in the detection process. Eggs are often clustered together and may have a sticky residue that helps them adhere to surfaces.
Factors Affecting the Egg-Laying Process
Several factors can influence where and how many eggs a female bed bug will lay. These include the availability of blood meals, environmental conditions like temperature and humidity, and even the presence of chemical residues from previous pest control attempts. For example, a study from North Carolina State University revealed that cooler temperatures could slow down the egg-laying process, while warmer conditions expedite it.
By being vigilant about inspecting potential egg-laying sites and understanding the factors that influence this process, you’ll be better equipped to disrupt the bed bug life cycle at its most vulnerable stage. In the next section, we will discuss the astonishing rate at which bed bugs can multiply, emphasizing the urgency of taking swift action.
The Astonishing Rate of Bed Bug Multiplication
If you’re still pondering the urgency of tackling a bed bug problem, consider this: The speed at which these pests can multiply is nothing short of astonishing. Recognizing the rate of multiplication is vital, as it underscores the need for prompt and comprehensive action. Failing to act in a timely manner could lead to a minor problem ballooning into a full-blown infestation.
How Many Eggs Can a Female Lay?
As mentioned earlier, an adult female bed bug can lay up to five eggs per day under optimal conditions. Given a lifespan of several months to about a year, a single female can lay hundreds of eggs. These numbers might sound alarming, but they serve to emphasize the necessity of prompt action to halt reproduction.
Exponential Growth: When One Becomes Hundreds
The situation becomes more alarming when you consider that the newly hatched nymphs can reach reproductive maturity in as little as three weeks, given adequate feeding. Consequently, what starts as a small colony of a few bed bugs can explode into a major infestation comprising thousands of individuals in a matter of weeks.
Real-world Implications: Why Time is of the essence.
Given the rapid reproductive rate, even a small delay in treatment can result in a significantly larger and more challenging problem. An infestation that might initially require minimal intervention can quickly escalate to a situation necessitating professional extermination services, increased financial burden, and extended treatment time. A 2011 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasized that bed bug infestations can spread rapidly within multi-unit housing structures, further highlighting the need for swift action [source].
The takeaway here is clear: Time is of the essence when dealing with bed bugs. The longer you wait, the more challenging and costly the extermination process becomes. In our next section, we will explore effective strategies for controlling and eliminating bed bugs, arming you with the tools you need to act decisively.
Breaking the Cycle: Effective Bed Bug Control Methods
Realizing the rapid rate of bed bug multiplication underscores the importance of timely and effective control measures. Let’s delve into the myriad of available strategies to halt this cycle of infestation, focusing on both chemical and non-chemical approaches. Knowing these methods will equip you with a comprehensive toolkit to tailor your attack against these persistent pests.
Chemical Treatments: Insecticides and How They Work
Chemical treatments, specifically insecticides, have long been a go-to option in bed bug control. These substances work by attacking the nervous system of the bed bugs, leading to paralysis and eventually death. However, due to increasing resistance among bed bug populations, it’s crucial to consult professionals about the most effective and currently recommended chemical treatments. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure not only effectiveness but also safety during application.
Non-Chemical Methods: Heat Treatment, Vacuuming, and Traps
If you’re looking to avoid chemicals, there are non-chemical strategies that can be equally effective when executed correctly. Heat treatment involves raising the temperature in the infested area to levels lethal for bed bugs. Usually around 122°F (50°C), a method supported by research from the University of Minnesota [source]. Vacuuming can also be an effective measure for removing bed bugs and their eggs from specific locations. Although it’s not a standalone solution. Traps, often used to monitor infestation levels, can also help in reducing bed bug numbers when used in conjunction with other methods.
Prevention: Barrier Techniques and Ongoing Vigilance
Ultimately, prevention is better than cure. Barrier techniques, such as mattress encasements and climb-up interceptors, can restrict bed bug movement, making it easier to target them. Regular inspections, proactive cleaning, and public awareness can go a long way in preventing an infestation from taking hold in the first place.
By understanding the different approaches to bed bug control, from chemical treatments to non-chemical alternatives, you can make informed decisions tailored to your specific situation. As we wrap up, the concluding section will summarize the vital points covered in this post. Reiterate the urgency of breaking the bed bug reproductive cycle for effective extermination.
Conclusion: Take Action to Break the Bed Bug Reproductive Cycle
We’ve journeyed through the complex world of bed bug reproduction. From understanding their basic characteristics to delving into their life cycle, mating behaviors, and rapid multiplication rates. More importantly, we’ve explored actionable strategies to control and eliminate these pests, both through chemical and non-chemical means. The urgency of breaking the reproductive cycle for effective bed bug control cannot be overstated. By taking proactive steps, you can prevent a minor issue from escalating into a full-blown infestation.
Summary of Key Points
To reiterate, understanding bed bug reproduction is pivotal for effective control. Knowing where they lay eggs, how fast they multiply, and how they mate provides invaluable insights for targeted extermination.
Next Steps: Additional Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into bed bug control, consult reputable sources like the EPA’s Bed Bug Information for guidelines on integrated pest management. Books and academic papers on entomology can offer more specialized knowledge for those interested.
The Time to Act is Now
Don’t wait until the problem spirals out of control. Implementing effective control methods right away is crucial for managing bed bug infestations. The sooner you act, the easier it will be to break the cycle and reclaim your living spaces.
By equipping yourself with this comprehensive knowledge, you’re not just learning facts. You’re arming yourself with the tools for effective bed bug extermination. Thank you for reading, and here’s to a bed bug-free future!




