Introduction
For many, the mere mention of bed bugs conjures images of itchy welts and restless nights. These tiny, stealthy insects have, over the years, gained fame for their biting habits. They often leave households in distress. While they’re tiny in size, their reputation looms large. Today, as we embark on an exploration into the world of bed bugs, we aim to shift from fear to understanding. So, how do bed bugs multiply?
These pests, which have coexisted with humans for centuries, have a fascinating life cycle. From their covert mating rituals to their surprising resilience. According to Entomological Society of America, bed bugs have been documented pests since ancient times, reflecting their deep-rooted presence in our lives. But what allows them to thrive? And more importantly, how do they multiply so effectively?
By delving deeper into their reproductive mechanisms, habitats, and behaviors, we can better arm ourselves with strategies to prevent and combat infestations. Whether you’re currently grappling with these pests or are just curious, this guide promises to be your definitive resource on all things bed bugs. Let’s peel back the sheets and reveal the hidden world of these nocturnal nuisances.
Life Cycle of Bed Bugs
Understanding how bed bugs multiply is akin to decoding their secret playbook. These pests undergo a series of transformations throughout their lives, each stage presenting unique challenges and vulnerabilities. Starting as minuscule, pearl-white eggs about the size of a pinhead, they often lay concealed in mattress seams, furniture joints, or even clothing. As these eggs hatch, out emerge the nymphs, which are juvenile bed bugs.
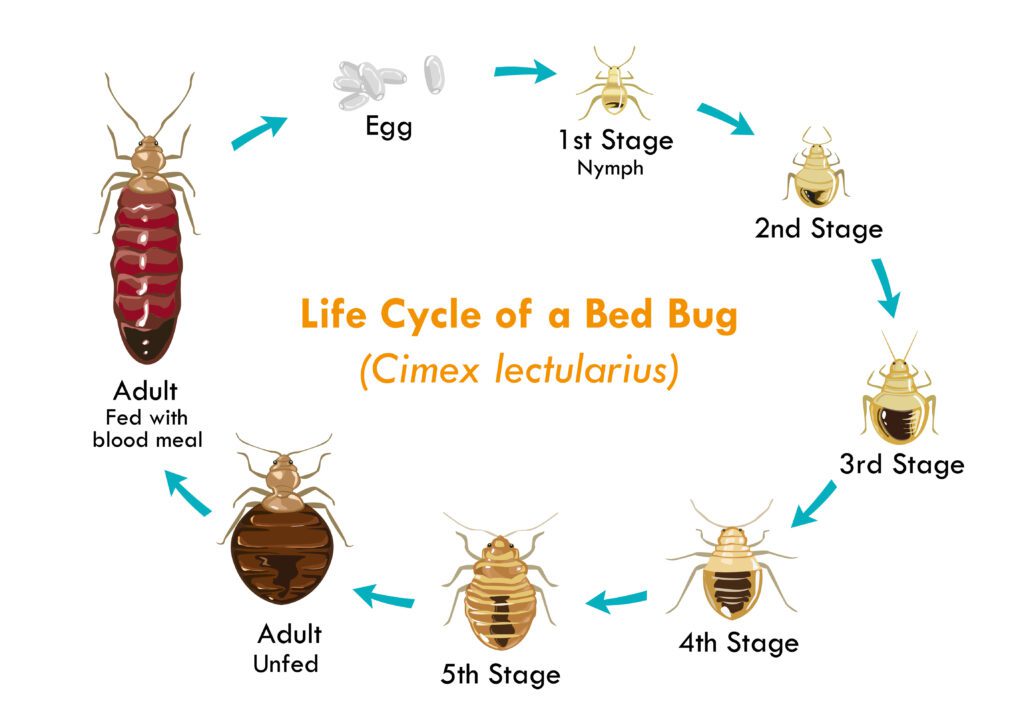
These nymphs undergo five distinct growth stages, shedding their skin at each juncture, a process known as molting. Depending on the conditions (like temperature and availability of food), it can take a nymph anywhere from 21 days to several months to mature into an adult. With every blood meal they consume, they move closer to maturity. Their color deepens, shifting from a translucent hue to a more evident reddish-brown as they age. Finally, they graduate into the adult phase. Adult bed bugs, with their flattened oval bodies, can live several months, sometimes even exceeding a year under optimal conditions.
According to a study from the University of Kentucky, their longevity is further extended if they have consistent access to blood meals and are housed in cooler environments. This deep dive into their lifecycle not only broadens our understanding but also helps us identify and target their weak points in our battle against infestations.
The Reproductive Habits
Diving into the world of bed bugs, it’s their prolific reproductive habits that often leave homeowners astounded. These insects have a unique mating procedure known as traumatic insemination. In this peculiar process, the male pierces the female’s body wall, bypassing her reproductive tract entirely, to deposit his sperm. While it might sound unsettling, this method ensures a high rate of successful impregnation.

After mating, a single female bed bug begins her role as a veritable egg factory. She’s capable of laying hundreds of eggs over her lifetime, often depositing them in hidden nooks and crannies, making eradication efforts more challenging. On average, a female lays 1-5 eggs per day and can lay up to 500 eggs in her entire life. The number of eggs produced often depends on the availability of blood meals. On average, a healthy female will lay a few eggs every day, ensuring the rapid expansion of their colony.
This reproductive prowess, combined with their stealthy habits, can lead to a full-blown infestation in a surprisingly short amount of time. The National Pest Management Association reveals that in just six months, a small bed bug problem can escalate into an overwhelming infestation of over 13,000 pests. Knowing how quickly these pests can multiply underscores the importance of timely intervention and thorough inspection.
Factors Affecting Bed Bug Multiplication
Bed bugs, though resilient, are not exempt from the influence of their surroundings. A variety of factors play pivotal roles in determining their multiplication rates and overall population growth. One of the primary drivers is the environmental conditions. These pests thrive best in temperatures ranging from 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C), although they can survive in both colder and hotter extremes for limited periods. The moisture level in their habitat also plays a part. Excessively dry conditions can be detrimental to their eggs, reducing their chances of hatching successfully.
Then, there’s the availability of food. Bed bugs are hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on blood. Human blood is their preferred diet, but in its absence, they’ll resort to feeding on other warm-blooded creatures like birds or rodents. The frequency of their meals impacts their reproduction; females need consistent blood meals to produce eggs. A well-fed female bed bug is a more prolific egg-layer than a starved one.
Lastly, while bed bugs have few natural enemies in the domestic setting, natural predators do exist in the wild. Centipedes, spiders, and some types of ants have been known to prey on bed bugs, limiting their numbers. This predatory factor, however, often plays a minimal role indoors, as these predators aren’t usually present in significant numbers within our homes. A comprehensive report by the Journal of Economic Entomology delves deeper into these influencing factors, shedding light on how even slight changes in their environment can drastically impact bed bug populations.
Signs of a Growing Bed Bug Infestation
One of the most unnerving things about bed bugs is their ability to remain undetected until their numbers swell to alarming levels. However, with a keen eye and informed knowledge, you can spot the early signs and take swift action. One clear indicator of their presence is physical evidence. This includes not just seeing the bugs themselves – which are roughly the size of an apple seed when fully grown – but also spotting their tiny, white eggs, often nestled in the fabric folds of mattresses or furniture. As nymphs grow, they shed their skins, leaving behind a trail of these translucent exoskeletons.
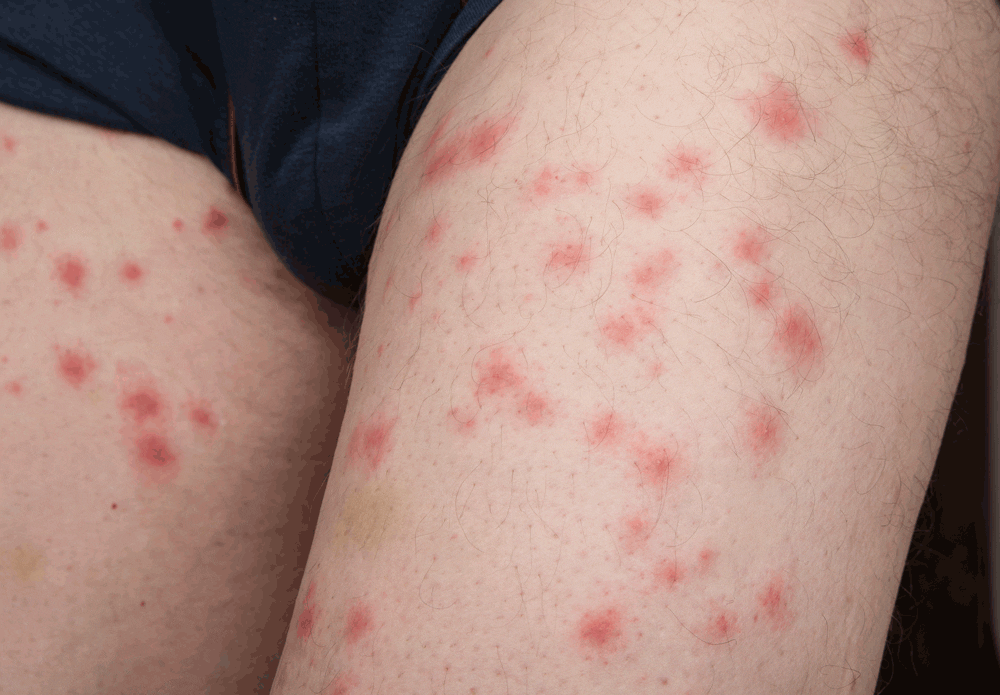
Another undeniable sign of bed bug activity is the presence of bite marks on the body. These bites are often in a line or cluster and can cause redness, itching, and inflammation. It’s important to note, however, that not everyone reacts to bed bug bites the same way; some may have minimal reactions, while others might exhibit severe allergic responses.
Additionally, bed bugs leave behind other telltale indicators. Their droppings, which appear as tiny black or brown dots, can often be found on bed linens or nearby walls. A more pronounced infestation might even produce a sweet, musty odor, emitted by the bugs’ scent glands.
For those who wish to delve deeper into the signs and scientific nuances of bed bug presence, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers a wealth of information, helping individuals differentiate between bed bug signs and other common household pests.
Effective Solutions to Combat Bed Bugs
Recognizing a bed bug infestation is one thing; successfully combating it is another. Fortunately, with the right approach, you can reclaim your living space from these persistent pests. Firstly, professional pest control should be at the top of your list. Experts in this field have the tools, knowledge, and experience to address infestations head-on. They can provide comprehensive treatments ranging from heat treatments to targeted pesticide applications, ensuring bed bugs at all life stages are effectively eradicated.
For those keen on DIY methods, there are several home remedies and over-the-counter products to consider. Diatomaceous earth, a natural insect killer, is known for its efficacy against bed bugs. It works by dehydrating the bugs, leading to their eventual death. Additionally, bed bug traps can be a valuable tool. While they won’t eliminate an infestation on their own, they can significantly reduce the number of active bugs and serve as a useful monitoring tool.
One often overlooked strategy is prevention. Investing in bed bug-proof mattress encasements, regularly inspecting hotel rooms when traveling, and being cautious about bringing second-hand furniture into your home can go a long way in keeping these pests at bay.
However, it’s vital to approach this issue with a blend of patience and persistence. Bed bugs are notoriously resilient, and multiple treatments may be necessary to achieve complete eradication.
Treatment Options for Bed Bug Bites and Infestations
When faced with a bed bug infestation, understanding your treatment options is paramount. This involves both addressing the bites these pests inflict and the larger task of eradicating the infestation itself.
Starting with bed bug bites, these irritating welts can cause varying levels of discomfort. Over-the-counter creams and antihistamines can effectively alleviate itching and inflammation. For individuals experiencing more severe allergic reactions, it might be wise to consult a medical professional for prescription remedies or advice. Keeping the affected area clean and resisting the urge to scratch can prevent secondary infections.
When it comes to treating the infestation itself, there are several avenues to explore:
- Heat treatment: This involves raising the temperature of the affected area to a level lethal for bed bugs at all life stages. Special equipment is used to ensure even heat distribution, making it an efficient, chemical-free solution.
- Pesticide applications: Several pesticides are EPA-approved for bed bug extermination. It’s essential, however, to always follow label directions and ensure the chosen product is specifically designed for bed bugs.
- Cold treatments: While bed bugs can endure cold temperatures, prolonged exposure to extreme cold can be fatal. Portable freezing equipment can be used, though this method may be less effective than heat treatments.
- Encasements: Using special protective covers for mattresses and pillows can trap bed bugs, cutting off their food source and eventually causing them to die.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): This approach combines various methods, from chemical treatments to preventive measures, ensuring a comprehensive solution to bed bug problems.
Remember, while DIY methods can offer temporary relief, for severe infestations, enlisting the help of professional pest control services often yields the best results. They can provide a tailored approach, factoring in the scale of the problem and the specific conditions of the infested area.
Conclusion: The Importance of Proactive Bed Bug Management
In our journey to unravel the mystery of how bed bugs multiply, it becomes evident that these tenacious pests, while small, can pose a significant challenge for homeowners. Their rapid reproduction rates, coupled with their resilience and adaptability, make them a formidable foe. However, as we’ve explored, a combination of knowledge, preventive measures, and effective treatment strategies can pave the way for a bed bug-free environment.

It’s crucial to remember that early detection and intervention are key. By understanding the signs of a burgeoning infestation and the factors that influence their multiplication, individuals can take proactive steps to curb their spread. Whether it’s the investment in preventive measures like mattress encasements or seeking professional pest control assistance at the first sign of trouble, proactive action can make all the difference.
Bed bugs might have enjoyed a resurgence in recent decades, but with the wealth of information available and the myriad of treatment options at our disposal, there’s every reason to believe we can turn the tide against them.




